Basics of Virtualization
Virtualization consists of allowing one set of hardware to host multiple virtual machines. It is in use at most large corporations, and it is also becoming more common at many small organizations, businesses.
It means the creation of virtual resources (memory, storage, processor) rather than actual resources like hardware, OS, etc.
We can use virtualization at our home pc (personal computer). We can use one or more virtual machine in a single system. Virtual machines with different operating system can run on the same physical machine or server.
The virtualization software sits directly on the top of the hardware or bare metal. It allows guest operating system such as windows server, linux (Red Hat, Ubuntu, Cent OS).
A common example of virtualization is like:-
Partition of the hard drive to create separate hard drives.
There are different types of virtualization takes place such as;
- Desktop Virtualization
- Application Virtualization
- Server Virtualization
- Storage Virtualization
- Network Virtualization
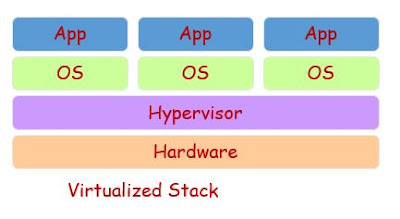
Hypervisor:
The application or software or hardware through which virtualization can be done or virtual machine (VM) can be created, run or managed is called a hypervisor. Many products such as VMware, Oracle virtual box, Microsoft hyper-v products offer hypervisor.
Host: The machine or the physical system who is running the VM is called the host.
Guest OS: Operating systems running on the host are called guest. Most hypervisors support 32-bit and 64-bit.
There are two types of hypervisors, Type-1 and Type-2
Type 1 hypervisors run on the system directly and sometimes called as bare metal hypervisor. They don’t need another OS to run within.
Type-2 hypervisors run as software within another OS.
Container based hypervisor: Container based hypervisor are those run services and applications in separate isolated containers within an OS. Each container is independent with each other to avoid interference. Machine’s OS and Kernel both run the services or applications within the container.
The prime benefit of container-based virtualization is it uses less resource and have more efficient and speed. But the container has to use the OS of the host system only.
It automates the orchestration, monitoring and management of log, load balancing, virtual network management, security patch management, security tools and controls.
Advantages of Virtual Machines (VM)
- Run operating systems where the physical hardware is unavailable.
- Easier to create new machines, backup machines, etc.
- Software testing using “clean” installs of operating systems and software.
- Emulate more machines than are physically available.
- Timeshare lightly loaded systems on one host.
- Debug problems (suspend and resume the problem machine).
- Easy migration of virtual machines (shutdown needed or not).
- Run legacy systems.
- Hardware-independence of operating system and applications.
- Virtual machines can be provisioned to any system.
-DR

No comments:
Post a Comment