Basics of SAN (Storage Area Network)
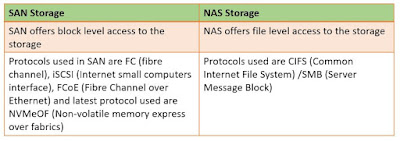
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a computer network that provides network access to storage. The storage is designed in a block level data storage solution. It has high speed architecture and connected the LUN (Logical Disk Units) of servers. They are resilient and help in removing single point of failure.
SANs are typically configured of hosts, switches and storage devices that are connected each other using technologies and protocols. SANs are commonly based on Fibre Channel (FC) technology that utilizes the Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) for open systems. Several disks and tape libraries are interconnected in a SAN system.
There are several types of interfaces used for SAN:
- FC (Fibre Channel)
- ISCSI (Internet small computer systems interface)
- FCoE (Fibre channel over ethernet)
- FC-NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express over Fibre Channel)
NAS
Similarly, NAS (Network Attached Storage) manages the storage centrally by sharing with other attached servers. But NAS works on ethernet only. It stores data as file system. NAS supports protocols such as NFS (Network File System) and Common internet file services/ server message block (SMB).
SAN and NAS both provide shared, centralized external storage which can be accessed by other devices over a network at the single time.
A storage and Controller
A storage system have all combination of Motherboard, CPU, DRAM, Memory, Network Control Card etc. All these components remain in a single frame known as controller. Controller is the brain you can can say. The storage controller is also known as head.
The storage system have disk sub system where it have disks, to store data. The disk sub system is being kept in same chassis or it can be kept at outside as external disk shelves.
Like, system and server a Storage system requires operating system to run. That OS is kept in the controller to control the communication out to the clients over the network and also to disk shelves. Those OS are proprietary to the manufacturer.
Benefits of using SAN and NAS:
- The benefits of using extra High Performance, scalability and availability. They increase storage utilization and improve data protection and security.
- Rather than direct attached storage it offers improved disk utilization.
- Devices and applications can be allocated storage as required and later it can altered.
- The external storage offers greater performance and capacity as data can be striped across many disks in an enterprise class storage system.
- This cutting edge technology offers resiliency that means, there's no single point of failure for the mission critical data available. If due to any incident, and any single component fails, there's another component or another backup to take its place immediately.
- Centralized storage management
- Storage tiering (Storage tiering is a key aspect of a storage tiering architecture that offers different technologies and is to classify data into levels of importance and assign it to the appropriate storage tiers for future retention. The organization shall classify its data accordingly. The older data can move to lower tier or archived than the newer data).
There are different types of storage media such as hard disk drives (HDD), that are available for both direct attached storage in your servers and for external SAN and NAS storage systems. Another type is known as a solid-state drive (SSD). SSDs are newer, faster technology than HDD technology as it has got no platter or moving parts. For which it works speedily. The SSD are also known as flash in enterprise storage environments. So, if someone says we need flash storage for latest technology, it’s nothing only SSD. SSD drives provide the highest performance, so they are expensive now with respect to the size of SSD, whether its 1GB or 2GB.
Storage Array:
A storage array is a data storage system for block-based storage, file-based storage, or object based storage. It is also called disk array. Instead of storing data on a server, storage arrays uses multiple drives in a collection of HDD or SSD disks capable of storing a big amount of data and are managed by a central management system.
-DR

No comments:
Post a Comment