Basics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is an internet based service that provides on demand access to shared computer.
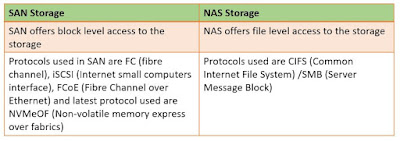
Cloud computing is hosting, computing services and data storage on the Internet cloud instead of hosting it locally and directly manage by user. It was derived generally from distributed computing. It can be further distinguished in to IAAS, PAAS, SAAS service models as per its implementation and roll out worldwide.
Example of cloud services:
- Microsoft one drive, Google drive, Drop box: Used to save images, videos, documents at cloud.
- Office 365: working on word, excel, power point on online mode.
There are many vendors provide cloud service now a days such as Amazon web services (AWS), Oracle cloud, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, VMware cloud etc.
Service Models
Iaas (Infrastructure as a service):
The Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) model utilizes virtualization or virtual infrastructure and customer pay the CSP (cloud service provider) for the resources used. Because of this, the IaaS model closely resembles the traditional utility model used by electric, gas, and water providers.
Paas (Platform as a service):
The Platform as a Service (PaaS) model is also known as cloud platform services. In this model, vendors allow multiple applications to be created and run on their infrastructure for different kind of services. One example is Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Saas (Software as a service):
The Software as a Service (SaaS) model is when users generically think of cloud computing. In this model, applications are remotely run over the web.
One of the advantages is that no local hardware is required, and no software applications need to be installed at own premise. The costing is calculated as per the subscription. We can say, this helps to avoid the upfront cost and complexity of maintaining the infrastructure. Again, scaling is another benefit of using cloud computing, you can use memory, storage, processor as per your business requirement.
Summary of Benefits of using cloud computing: Speed, productivity, performance, reliability, cost and security.
There are three type of cloud used: public, private and hybrid.
Public cloud is operated by third party organizations. Private cloud is operated by single business owners and it can be located at its own DC. Hybrid cloud are combination of both public and private cloud features.
Similarly it is divided for deployment model such as
- Private Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
Private Cloud model:
- It have single tenant implementation.
- Owned and operated by IT organization.
- Firm have their own data management policy in place.
- Self service and automation capacity.
Public Cloud
- It have multi tenant implementation.
- Public cloud is owned and operated by service provider ideally.
Hybrid Cloud
Combination of both private or more public clouds is known as hybrid cloud.
Benefits:
Cloud computing enables companies and applications, which are system infrastructure dependent, and to be infrastructure-less.
By using the Cloud infrastructure on “pay as used and on demand”, all of us can save in capital and operational investment.
Advantages of cloud Computing:
Lower Computer Costs
- You do not need a high-powered and high-priced computer to run cloud computing's web-based applications.
- Since applications run in the cloud, not on the desktop PC, your desktop PC does not need the processing power or hard disk space demanded by traditional desktop software.
- When you are using web-based applications, your PC can be less expensive, with a smaller hard disk, less memory, more efficient processor.
- In fact, your PC in this scenario does not even need a CD or DVD drive, as no software programs have to be loaded and no document files need to be saved.
Improved Performance
- With few large programs hogging your computer's memory, you will see better performance from your PC.
- Computers in a cloud computing system boot and run faster because they have fewer programs and processes loaded into memory.
Reduced software cost
- Instead of purchasing expensive software applications, you can get most of what you need for free.
Reliability
- Present cloud computing offer minimum or zero downtime in continuous operation to meet the exact SLA in the business.
Scalability
- Applications in the cloud can be scaled either vertically or horizontally. In case of vertical scaling, the computing capacity is being increased by increasing the RAM, CPU to the virtual machine (VM) and in case of horizontally scaling, the computing capacity can be increased by adding the no of instances or we can say increasing more VMs.
Disaster Recovery
- The data hosted at cloud can be replicated and a its back up can be taken in the cloud for safe guarding your data that can be accessed in case of any disaster or system crash situation.
RaaS: Recovery as a Service
A new model, even introduced keeping eye on the disaster recovery. In this cloud model, an organization keeps its data and IT infrastructure backup with a third party cloud computing party. RaaS solutions allow companies to recover applications and data such as files and databases in case of disaster. These service provide disaster recovery, backup and business continuity so that an organization can reduce downtime due to some major failure such as a hurricane, earthquake, fire, flood etc. In view of some tech firms, its also known as Disaster Recovery As A Service (DRaaS). A DRaaS mirrors a complete infrastructure in fail-safe mode on virtual servers, including compute, storage and networking functions. Again it comes with three models such as Managed DRaaS, Assisted DRaaS and Self-Service DRaaS.
-DR